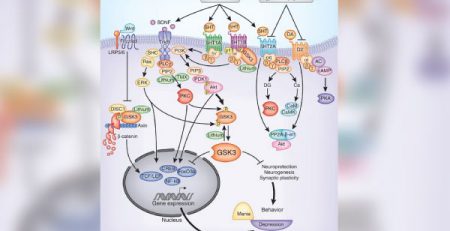
Smoking in early adulthood is prospectively associated with prescriptions of antipsychotics….
Rognli EB, Bramness JG, Von Soest T. Smoking in early adulthood is prospectively associated with prescriptions of antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, antidepressants and anxiolytics. Psychol Med. 2021 Feb 15;1-10. Online ahead of print.
“Daily smoking with high dependence in 2006 at age 28.5 (s.d. = 2.0) was associated with filling prescriptions of antipsychotics (OR, 6.57, 95% CI 2.19-19.70, p = 0.001), mood stabilizers (OR, 7.11, 95% CI 2.51-20.15, p < 0.001) and antidepressants (OR, 1.91, 95% CI 1.13-3.23, p = 0.016) 1-9 years later… Conclusions: In this study of young adults, daily smoking with high dependence was associated with later prescriptions of antipsychotics, mood stabilizers and antidepressants, indicating smoking as a risk factor for mental disorders treated with these drugs.”
Comment: Mental disorders are often found associated with smoking and this appears to be the case for both smokers and e-cigarette users. Stephen Hamann
Stephen Hamann