Initial findings of e-cigarette use and Covid-19 among adolescents
Benowitz NL, Goniewicz ML, Halpern-Felsher B, et al. Tobacco product use and the risks of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19: current understanding and recommendations for future research. Personal view. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. Volume 10, Issue 9, 900-915. September 1, 2022. Published: Aug 16, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00182-5
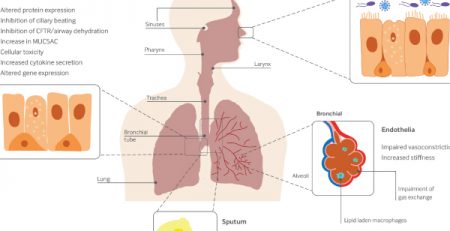
Authors reviewed 236 epidemiological studies of tobacco use and COVID-19 published from the start of the COVID-19 pandemic to Aug 30, 2021. They listed only six studies that included e-cigarette use, and the authors suggest more extensive research to answer questions about e-cigarette product use and risk of Covid-19 infections. They found only one study that focused on adolescents and young adults (Gaiha et al. 2020), which reported a five-times or more increased likelihood of a COVID-19 diagnosis among ever-users of e-cigarettes only (OR 5·05, 95% CI 1·82–13·96), ever-users of both e-cigarettes and cigarettes (6·97, 1·98–24·55), and past 30-day users of both e-cigarettes and cigarettes (6·84, 2·40–19·55).
Comment: Initial studies show that conventional smoking and e-cigarette use play a role in Covid-19 infections, although additional epidemiological studies are needed.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(22)00182-5/fulltext
Stephen Hamann